Traditional security operations center monitoring and rules-based alerts can only go so far against stealthy adversaries. What you need is a team of cyber hunters, constantly on the prowl for subtle signs of compromise. This is threat hunting. Threat hunting is the process of proactively searching for signs of compromise in an environment.
In this blog post, we're going to dive into threat hunting and how it can help your organization.
Understanding Threat Hunting
Threat hunters look for anomalies and signs of foul play that automated tools may have missed. Things like unusual network connections, strange process behavior, or signs of privilege escalation. The key is knowing what “normal” looks like in your environment so you can spot the abnormal.
While most cyber defense is reactive, threat hunting is a proactive approach to cyber defense that involves seeking out malicious activity that may have evaded detection. It usually begins with the assumption or a hypothesis that a system has been compromised, and then a team of experts searches for the evidence that supports that hypothesis.
Threat hunting requires pouring over tons of data from sources like firewalls, endpoints, servers, and cloud services. Human analysts will use tools to analyze logs, packets, memory dumps, and more. The goal is to piece together clues and uncover visibility gaps by the SOC or other logging methods to identify compromise, track adversaries, and disrupt their activities before major damage is done.
Effective threat hunting also relies on context about the latest techniques, tools, and procedures used by attackers. Threat intelligence feeds help hunters stay on the cutting edge so they know what to look for. Pairing cyber threat intelligence with data analysis and visualization tools gives threat hunters the best chance of finding threats that may be slipping through the cracks.
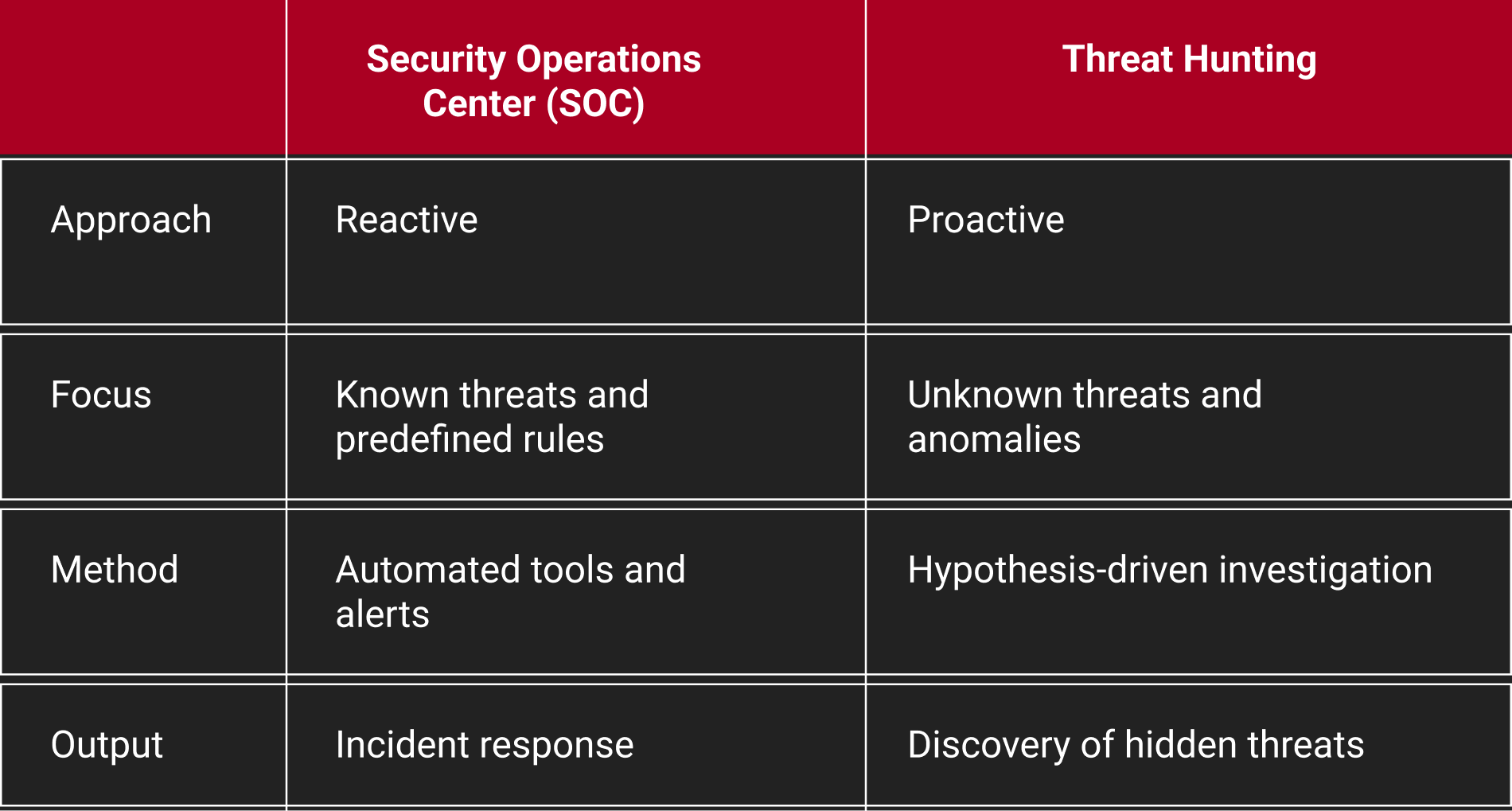
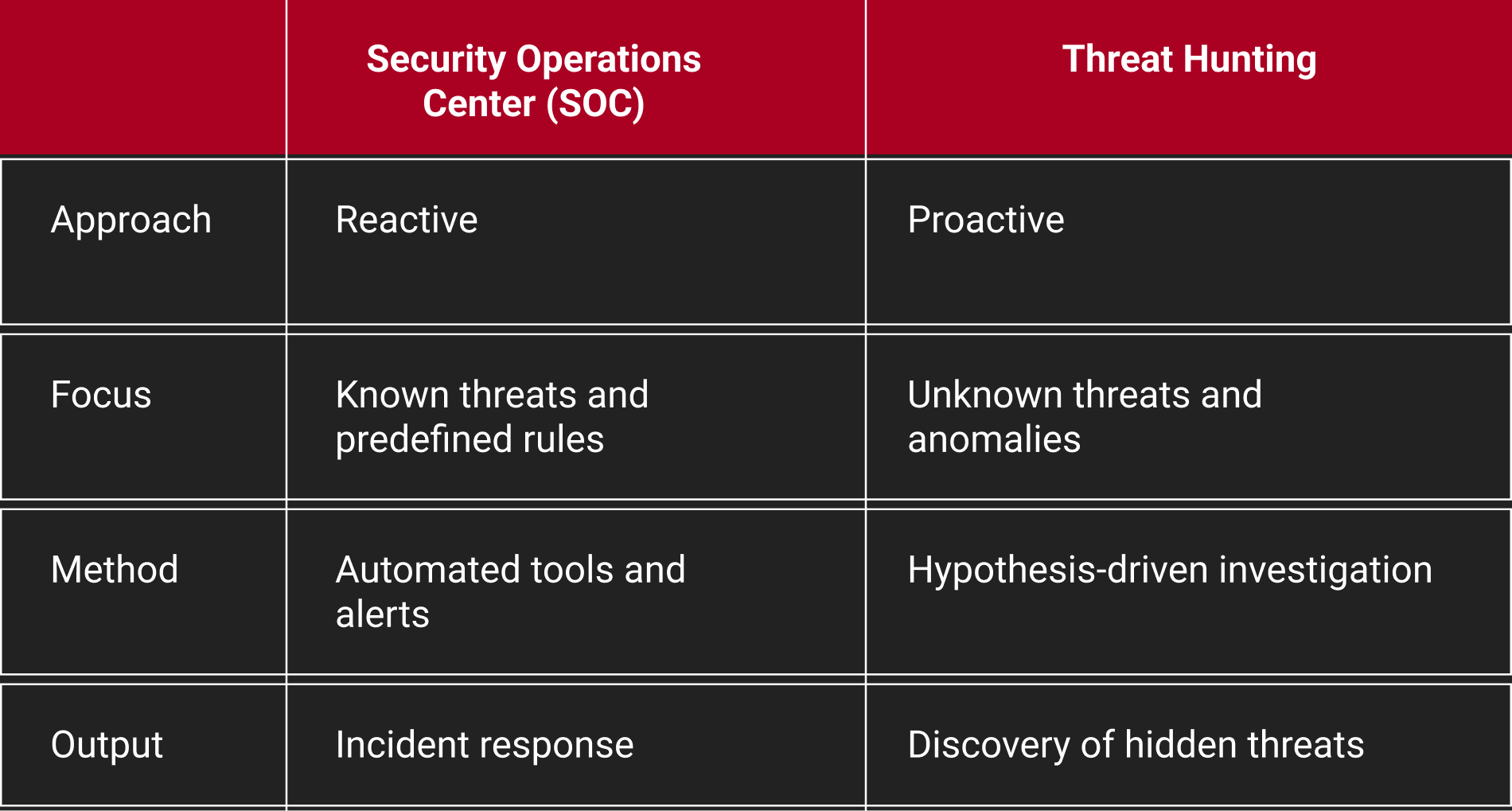
SOC vs Threat Hunting
Security Operations Centers (SOC) and Threat Hunting represent distinct approaches. SOC relies on predefined rules and tools and is a reactive approach to security. Conversely, Threat Hunting adopts a proactive, research-focused strategy, actively seeking both known and unknown threats. This agile approach proves more effective in the dynamic cybersecurity landscape. The key distinction lies in SOC's reactive response to known indicators, while Threat Hunting proactively searches for potential threats.
Threat Intelligence vs Threat Hunting
Threat hunting refers to actively searching your network for signs of compromise or intrusion, even without a specific threat indicator. It’s a proactive approach to cyber defense that involves manual searching and anomaly detection.
Threat intelligence, on the other hand, refers to gathering information about potential adversaries and their tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs). This includes researching hacker groups, monitoring cybercrime forums, and analyzing malware. Threat intelligence provides context that helps focus your threat-hunting efforts.
Some key differences:
- Threat hunting is an active process of searching your environment for threats. Threat intelligence involves passively collecting information about threats outside your network.
- Threat hunting is performed by your cybersecurity team. Threat intelligence can come from both internal research as well as external sources like government agencies, industry groups, and cybersecurity firms.
- Threat hunting searches for signs of compromise in your own systems and network. Threat intelligence looks at the broader threat landscape, including adversaries’ motives, targets, and attack methods.
- Threat hunting uses tools like security information and event management (SIEM) systems, endpoint detection and response (EDR) software, and network sniffers to analyze your environment. Threat intelligence relies more on open-source research and human analysis.
To be effective, threat hunting should be guided by threat intelligence.
Key Elements of Effective Threat Hunting
To hunt threats effectively, you need the right tools and techniques. Here are the key elements:
- Comprehensive Data Sources
Data is the backbone of every hunt. The more diverse and rich your data sources—like network traffic, logs, and endpoint telemetry—the more insights you can gain. Remember, more data means more opportunities to uncover hidden threats. - Actionable Threat Intelligence
Threat intelligence adds valuable context to your hunts by highlighting potential adversaries, their tactics, and indicators of compromise (IOCs). It’s the perfect complement to hunting, helping you prioritize efforts and detect threats faster. - Strong Analytical Skills
Great threat hunters don’t just rely on tools—they leverage their analytical expertise to identify anomalies and uncover patterns. Tools with data visualization and advanced query capabilities are critical, but skilled analysts make the magic happen. - Proven Methodologies
Frameworks like MITRE ATT&CK and the cyber kill chain are essential roadmaps for effective hunts. They systematically outline adversary behavior and guide you to detect threats at every stage of an attack. - The Human-AI Partnership
Machine learning and AI can accelerate the hunt by identifying anomalies and crunching vast datasets. However, human intuition is irreplaceable. Analysts ask the right questions, connect the dots, and assess the broader impact of potential threats. - Continuous Improvement
Threat hunting is a journey, not a one-time task. Regularly evaluate your hunt results, refine methodologies, and enhance tools and data sources. Updating your threat intelligence ensures your team stays one step ahead of evolving adversaries. - Commitment to Excellence
Successful threat hunting requires dedication, persistence, and a hunger to learn. Every hunt contributes to a growing knowledge base, sharpening your skills and improving future outcomes.
Framework and Methodology in Cyber Threat Hunting
Frameworks and methodologies provide threat hunters with a structured approach to searching for threats. One of the most well-known frameworks is the MITRE ATT&CK framework.
The MITRE ATT&CK framework catalogs known adversary tactics, techniques, and procedures in a comprehensive matrix. Threat hunters can use the framework to determine where in the attack lifecycle an adversary might be operating and focus their hunt accordingly. The framework is also useful for mapping detected threats to known adversary behavior.
While there are other frameworks to choose from including Lockheed Martin, Hunt Evil Framework, and more, MITRE ATT&CK is an industry standard and is used by most organizations.
Following are some common methods used by threat hunters:
- Hypothesis-Based Hunting: Involves formulating hypotheses based on known threats or suspicious activities and actively investigating to confirm or refute them.
- IOC-Based Hunting (Indicators of Compromise): Focuses on searching for specific indicators that may indicate a security incident, such as IP addresses, file hashes, or patterns associated with known threats.
- TTP-Based Hunting (Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures): Centers on understanding and identifying the tactics, techniques, and procedures commonly employed by adversaries, allowing for the detection of unusual or malicious behavior.
- Threat Intelligence-Driven Hunting: Utilizes external threat intelligence sources to inform and guide the hunting process, incorporating information about emerging threats and adversary behaviors.
- Behavioral-Based Hunting: Focuses on analyzing patterns of behavior, both normal and abnormal, to detect subtle indicators of compromise or malicious activities within the network.
Challenges in Threat Hunting
Threat hunting isn’t easy. It requires time, resources, and a commitment to continuous improvement. Some of the biggest challenges threat-hunting teams face include:
- Lack of context: Without sufficient context about systems, networks, and normal behavior, hunters may chase false positives or miss real threats. Build context over time and tap into threat intel.
- Access to data: Sometimes, threat hunters don't get the data they require from their organization due to slow processes within the organization. Or the data they get access to is of poor quality and not actionable. This can hinder the threat hunting process because you can't look for the needle in the haystack if you don't have a haystack, to begin with.
- Missing expertise: Threat hunting requires specialized skills like intrusion analysis, forensics, and malware reverse engineering. Hire experienced hunters or invest in ongoing training. Moreover, threat hunters must understand where, how, and what to search for.
- False positives: Often during their hunt, threat hunters will see a lot of false positives before they find an actual threat.
Best Practices for Effective Threat Hunting
1. Pick the Right Starting Point: Begin by identifying critical assets and sensitive data within your network. This ensures a targeted and efficient threat hunting process, focusing efforts where they matter most.
2. Knowing Attacker's TTPs: Understanding the Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs) commonly used by attackers is crucial. This knowledge guides threat hunters in recognizing unusual patterns or behaviors that deviate from the typical methods employed by adversaries.
3. Establish a Baseline for Normal Behavior: Create a baseline of normal network behavior. This involves understanding typical patterns of user activity, system interactions, and network traffic. Deviations from this baseline can signal potential threats that require investigation.
4. Define Scope, Roles, and Desired Outcomes: Clearly define the scope of your threat hunting activities, roles of team members, and desired outcomes. This ensures a focused and coordinated effort, preventing unnecessary diversions and enhancing the effectiveness of the hunt.
5. Leverage Automation to Enhance the Process:
Use automation tools to streamline repetitive tasks and analyze large volumes of data efficiently. Automation enhances the threat hunting process by allowing analysts to focus on more complex and strategic aspects of the investigation.
The Role of ML and AI in Threat Hunting
Machine learning (ML) is reshaping the future of threat hunting by swiftly analyzing vast datasets, uncovering patterns, and identifying anomalies indicative of potential threats. With the ability to detect unknown threats by analyzing historical data, ML-driven solutions streamline the threat hunting process, generating high-fidelity leads for quick investigations. The integration of ML with Managed Detection and Response (MDR) data empowers threat hunting groups to identify behavioral patterns and stay ahead of emerging threats. Beyond threat detection, ML enhances incident response by providing rapid analysis, contextual information, and actionable insights, freeing up human analysts for more strategic tasks and mitigating burnout issues in the security industry. ML can be a vital tool for context-rich insights that can help strengthen your defenses against evolving and emerging threats.
AI's strength lies in predictive analytics, utilizing algorithms to analyze past incidents and forecast potential future threats. This proactive approach empowers organizations to outpace cybercriminals, anticipating and mitigating risks before they manifest. Furthermore, AI-driven systems facilitate real-time responses, continuously learning from data patterns to identify subtle irregularities indicative of potential threats. As AI evolves, its contribution to threat detection and prevention will enable human threat hunters to focus on the most sophisticated threats, enhancing overall cybersecurity resilience.
However, despite the benefits these tools offer, human judgment will remain indispensable in threat hunting. While AI and machine learning enhance the efficiency of identifying patterns and anomalies, the nuanced understanding, context, and strategic decision-making capabilities of human analysts are crucial for interpreting complex scenarios, adapting to evolving threats, and ensuring a comprehensive and accurate threat assessment.
Conclusion
While threat hunting requires effort and resources, the benefits of gaining visibility into threats that have evaded your defenses are huge. Staying on the cutting edge of techniques, tools, and intelligence will help ensure your threat hunts are as effective as possible. At Threat Intelligence, we've got the right combination of experience and technology to help you outsmart the bad guys. With automated capabilities ranging from intelligence gathering to alert triage, we can help you enhance your threat-hunting capabilities. And with a team of Black Hat certified security experts, you can rest assured that no threat goes unnoticed.
Book a demo with us today and empower your organization to stay ahead of emerging threats. Safeguard your digital assets—Explore
Evolve now.






