OT and SCADA systems are the beating heart of critical infrastructure, controlling everything from the electric grid to water treatment facilities. But with increasing connectivity comes increasing risk. As these systems adopt standard IT technology, they become more exposed to cyber threats that could have devastating real-world effects. That's why penetration testing is so important.
Understanding OT/SCADA Systems
SCADA and OT systems are used to control and monitor industrial processes in a wide range of industries.
SCADA stands for Supervisory Control And Data Acquisition. It is a combination of hardware and software that allows you to automate industrial systems. They help monitor and control these systems and processes both locally and remotely by collecting and processing data from those systems.
According to Gartner, 'Operational technology (OT) is hardware and software that detects or causes a change, through the direct monitoring and/or control of industrial equipment, assets, processes and events.'
It's the hardware and software that detect and cause changes in the physical devices present in industrial control systems. It focuses on the industrial processes and operations and keeps them running 24/7.
Manufaturing, oil and gas, water and wastewater treatment, power grid management, are some of the many industries where OT and SCADA systems are used.
OT vs SCADA:
While OT and SCADA are closely related, they have different purposes. OT is an umbrella term used to describe the hardware and software that are used to manage industrial processes and operations. So SCADA is a part of OT.
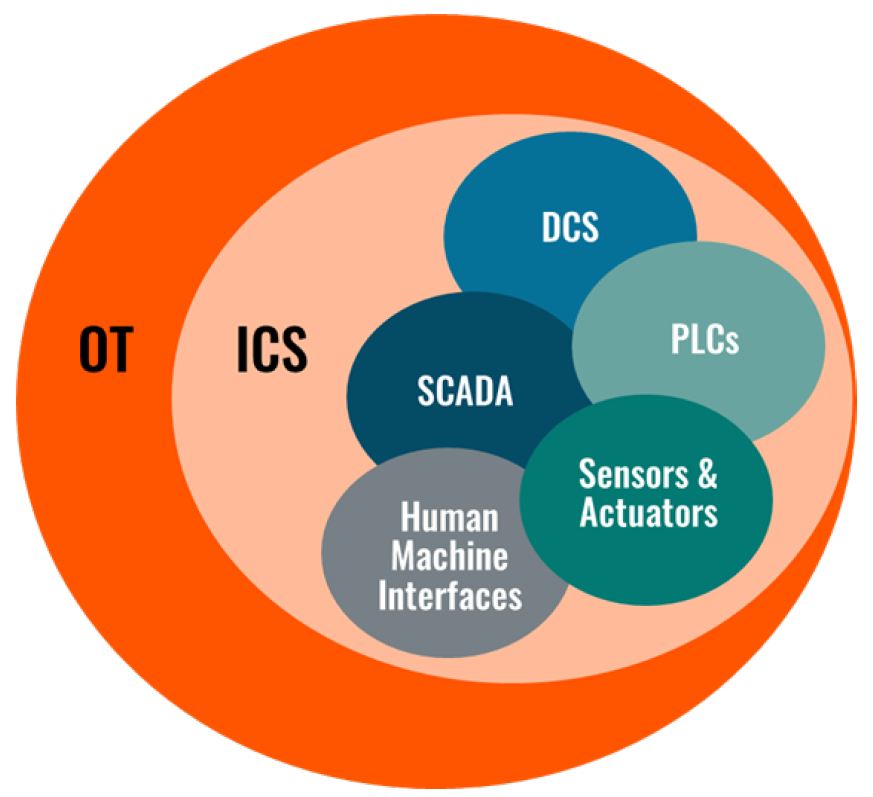
Source: ABI Research
SCADA is the part of OT that only focuses on monitoring and controlling processes in real-time. The main function of SCADA is to collect data from the Central Control and Command Centre.
Why Penetration Testing Matters for OT/SCADA
If you operate an OT or SCADA system, penetration testing should be a top priority. These systems control critical infrastructure like power grids, water treatment facilities, and transportation systems. As threats evolve and regulations tighten, testing is key to identifying and fixing vulnerabilities before they're exploited. Critical infrastructure protection is paramount in safeguarding these vital systems. For a more in-depth exploration of this topic, read our comprehensive blog post on the importance of critical infrastructure protection.

Evolving Cyber Threats
OT and SCADA systems were traditionally air-gapped, but many now have some level of connectivity, opening them up to cyber threats. Hackers, hacktivists, and nation-state actors target these systems to cause disruption. In addition, being interconnected means OT/SCADA systems also have exploitable vulnerabilities. Denial of Service (DoS) and ransomware attacks are especially common and can cause serious damage to critical infrastructure. In fact, attackers often target these systems because disrupting them can have huge real-world impacts.
In the first half of 2023, CISA revealed 670 vulnerabilities that affect industrial control systems (ICS) and other operational technology. In addition to unpatched security flaws, these systems also face other risks ranging from insider threats, compromised devices, human error and complexities introduced by IoT devices. Penetration testing can help you uncover these flaws before attackers get to them.
Meeting Compliance Requirements
Regulations like NERC CIP require utilities to assess and mitigate risk. Penetration testing checks that your OT security controls are functioning properly and helps ensure compliance. Regular testing also shows regulators your organization's commitment to security.
Gain Valuable Insights
Penetration tests provide an objective view of your OT security posture. Skilled testers mimic real-world attacks to uncover vulnerabilities and evaluate how well your team detects and responds to incidents. Their findings and recommendations help strengthen your cyber defenses and better prepare your team.
Penetration testing OT and SCADA systems before hackers strike allows you to:
- Identify and fix vulnerabilities like unpatched software, default passwords, and unencrypted communications;
- Improve network segmentation to limit the spread of attacks;
- Enhance monitoring to detect intrusions early;
- Update policies and procedures to account for new risks;
- Train staff on recommended security practices.
While testing does introduce some risks if not done properly, the potential benefits to critical infrastructure security far outweigh the costs. Regular penetration testing, along with good cyber hygiene and risk management, can help ensure the safe and reliable operation of the OT and SCADA systems we all depend on.
As threats intensify, penetration testing should be an integral part of any OT risk management strategy. Regular testing, along with continuous security monitoring and vulnerability management, will help keep your critical systems protected.
OT/SCADA Pen Testing Methodology
Penetration testing methodologies for OT/SCADA typically follow a similar process to IT systems. Testers start with information gathering to build a profile of the OT network and identify potential targets. This is done through open-source research, social engineering, and passive scanning. Any active scanning or exploitation is done carefully and incrementally to avoid system instability.
Passive Network Mapping
Passive network mapping involves observing traffic on the OT network to map connections between devices and systems. This can reveal network architecture, device types, communication protocols, and potential entry points. Passive mapping is a non-intrusive way to gather information before actively scanning the network.
Vulnerability Scanning
Vulnerability scanners are used to identify known security weaknesses in OT devices and software. Scans should be performed slowly while monitoring systems to avoid overloading aging components. Any critical vulnerabilities found should be addressed immediately.
Exploitation
The goal of exploitation is to gain access to systems and determine the level of access and control available. On OT networks, exploitation is done extremely carefully by security professionals with experience in ICS environments. Testers start with non-essential systems and slowly expand to critical infrastructure. The purpose is to demonstrate risk, not cause operational disruption.
Penetration testing of OT and SCADA systems requires specialized knowledge, training, and experience to balance security testing objectives with operational stability. When done properly, pen testing these critical systems provides valuable insight into real-world risks and helps organizations strengthen their security posture.
When it comes to testing OT/SCADA systems, our External Penetration Testing workflow is equipped to handle any infrastructure, including SCADA systems. Often, organizations aren’t even aware their SCADA systems are exposed. A comprehensive
external test can help identify these hidden risks and give you a clear picture of your security posture.
Best Practices for Safe and Effective OT/SCADA Penetration Testing
When it comes to penetration testing OT and SCADA systems, the approach can differ from traditional IT systems. Why? These systems have unique security risks and vulnerabilities and need to be available at all times. Any disruptions to critical systems can lead to serious, costly, and far-reaching consequences.
That's why when it comes to these systems, safety and ethics are top priority. Some best practices to keep in mind:
Do no harm
The cardinal rule of any penetration test is “do no harm.” Make sure testing does not disrupt critical operations or damage equipment. Start with non-intrusive methods like port scans and vulnerability assessments before attempting to exploit any systems. Have contingency plans in place in case anything goes wrong.
Obtain proper authorization
Always get written permission from system owners before conducting testing. Clearly define the scope and objectives to ensure all parties understand what will be tested and how. Authorization should come from executives who can approve any potential disruptions.
Balance Security Testing with Operational Stability
When testing critical infrastructure, minimizing disruptions is key. Ideally, you’d run tests in a non-production environment. But if that’s not possible, manual testing by experienced professionals is the safest route. Automated tools can sometimes cause issues, so manual testing ensures a more controlled, hands-on approach.
Have OT/SCADA expertise on your team
Penetration testing OT and SCADA systems requires specialized knowledge beyond typical IT systems. Include experts with experience in the specific hardware, software, and protocols used in the environment. They should understand how systems and devices interact so testing does not inadvertently impact critical operations.
Conclusion
While these systems are complex and testing them does come with risks if not done properly, following industry best practices and working with experienced professionals can help ensure a successful engagement. Regular testing is key to gaining visibility into evolving threats, meeting compliance standards, and ultimately strengthening your organization's security posture. Now that you understand what's at stake and have a roadmap to get started, it's time to take action.
Contact us today to schedule your assessment and ensure your systems are secure.








