Some of the biggest hacks of all time have started off as a phishing email. They didn’t involve purchasing zero-day exploits on the black market, encryption, or any other sophisticated hacking technique, rather they simply relied on human error.
Today, phishing attacks have reached a record-high with latest statistics showing that these attacks are responsible for over 80% of reported security incidents.
Continue reading to learn more about how this popular social engineering attack works, how to prevent it, and some of the biggest scams in cybersecurity history.
What Is Phishing?
Phishing is a type of cyberattack that uses disguised emails, calls, or text messages to trick targets into revealing sensitive personal data like their personally identifiable information, banking and credit card details, and passwords.
The term “phishing” was coined after the 1996 hacking of America Online. The hackers were using a deceptive email as bait to “fish” for customers that would give up their personal information. Hackers frequently substitute the letters “ph” for the letter f, a reference to the original form of hacking known as phone phreaking.
How do Phishing Attacks Work?
Phishing attacks typically start off with a fraudulent email that appears to be coming from a reputable source. Once the victim falls for this, he/she is lured into giving up personal and confidential information, usually on a scam website. Occasionally, attackers will get targets to download malware into their system through malicious email attachments.
Besides individual attacks, these social engineering tactics are often used to trick employees into providing critical company data which is then used to attack the company. Phishing is a common starting point for cyberattacks such as advanced persistent threats (APTs) and ransomware.
Recent reports suggest that phishing attacks compromise mainly three types of data: credentials, personal data and medical data.
Types of Phishing
Email Phishing
This is the most common type of phishing attack, where a fake email is sent to millions of potential victims to see who takes the bait. Such email spoofing attacks are common, in which the email header is forged to make the message appear to have been sent by a verified sender. Every day, an estimated 3.4 billion phishing emails are sent.(Source:
Clario)
Spear Phishing
Spear phishing is different from email phishing in that the attacker chooses his victim. It is a targeted phishing attempt in which specific organizations or people are chosen rather than a large number of victims at random.
They are usually personalized and informal emails that contain information that is tailored to the victim to create the illusion of a real email from a trusted sender. These customizations can include a topic the target is interested in, or a recent event attended by the target or something similar. As per a recent
threat report
, nearly 65% of all known groups carrying out targeted cyber attacks use spear-phishing emails.
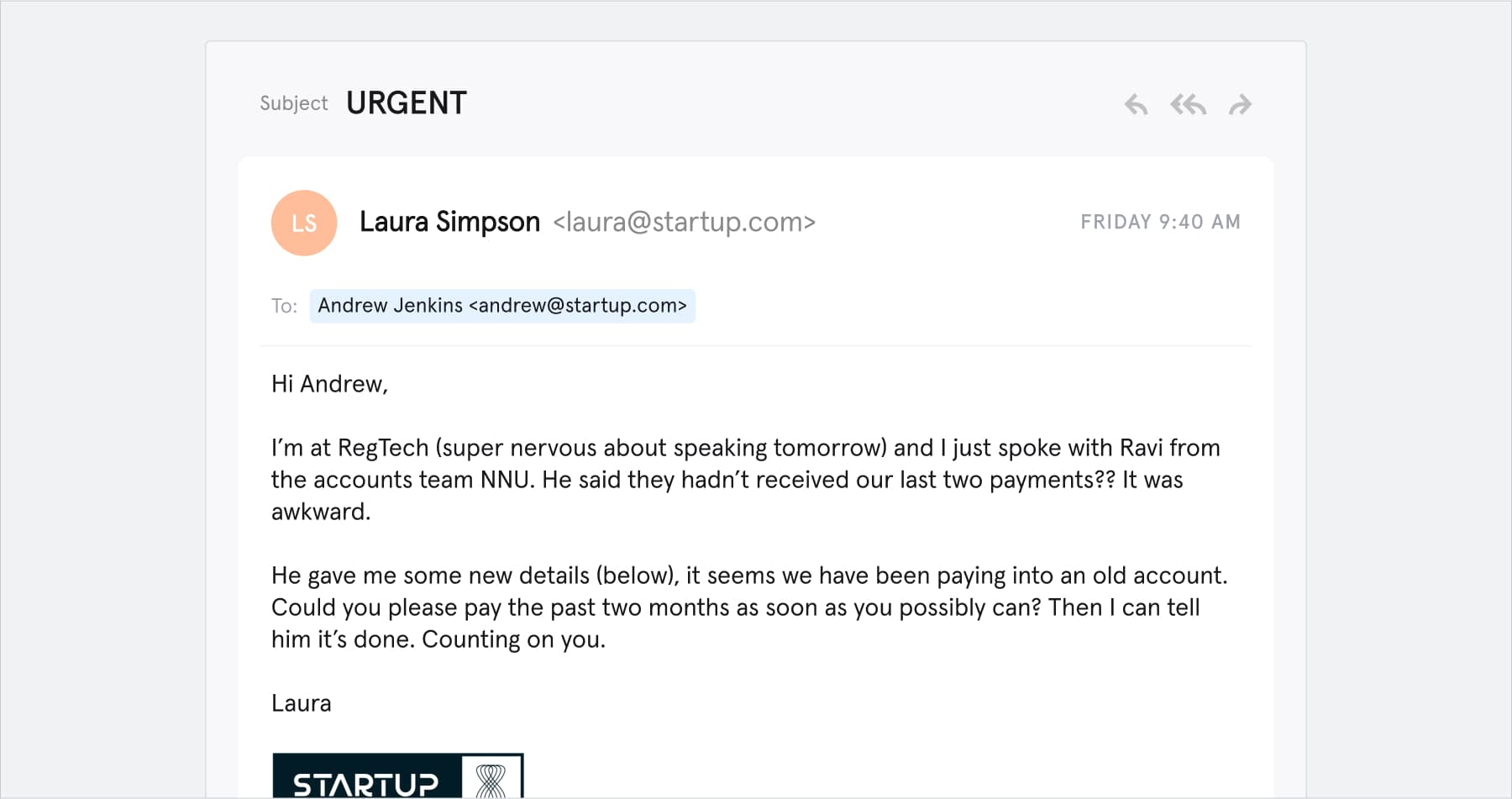
Whaling
Whaling is a more advanced version of spear phishing. A phishing attack that directly targets an enterprise's top executives is known as whaling. A lot of research goes into these attacks because the attackers need to find out who the target communicates with and the nature of their discussions. These targets are chosen because they are the “big fish” - high-value targets that have access to a large amount of sensitive information, compared to a regular employee.
For instance, the CEO of a company could be a potential target. As a result, such attacks are highly profitable for hackers. A lot of research goes into these attacks because the attackers need to find out who the target communicates with and the nature of their discussions in order to then craft a personalized scam email.
Vishing
Malicious actors also rely on other forms of communication to carry out phishing attacks. “Voice phishing”, otherwise known as Vishing, is phishing done over the phone. To launch a vishing attack, the attacker sets up a Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) server and then mimics legitimate entities in order to steal confidential data and/or funds. Common techniques attackers use to fool victims include using technical jargon, mumbling over the phone, and ID spoofing to disguise unknown phone numbers.
Smishing
Just like vishing, the smishing attack also involves the usage of phones to get a hold of the targets. Text messages that contain malicious links are sent to the targets to retrieve personal information.
We've all received an SMS that looks something like this:
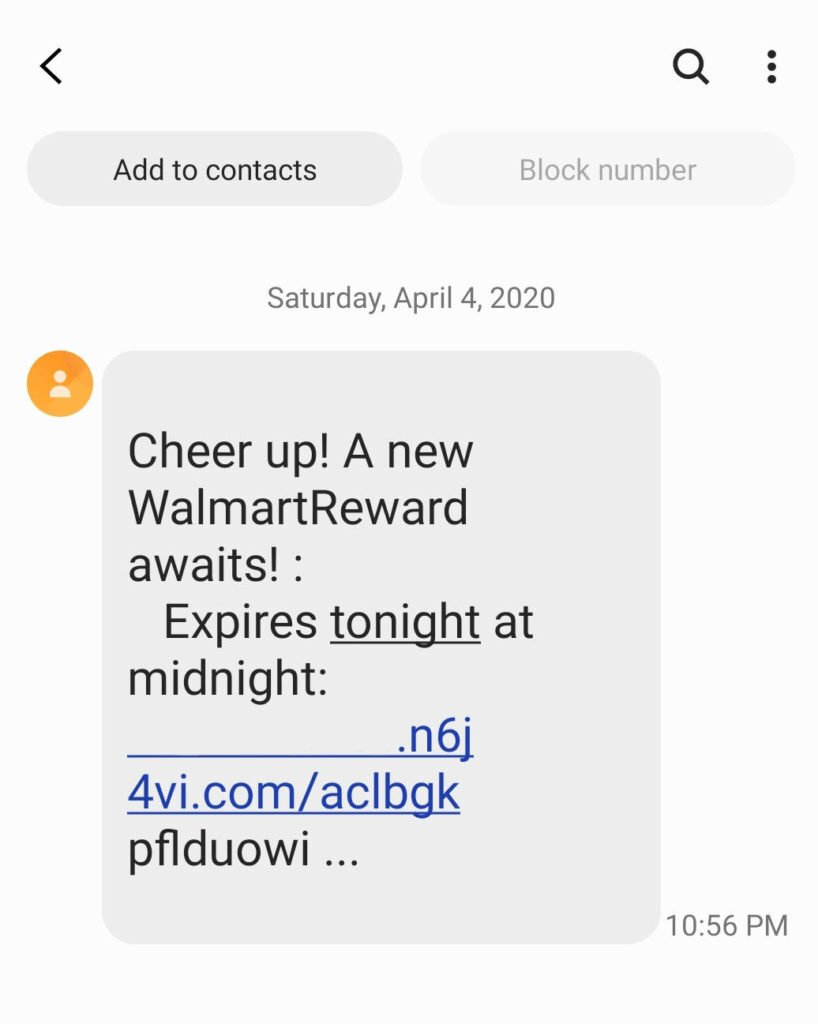
Source: Security Boulevard
Angler Phishing
The widespread usage of social media has given rise to a new type of phishing attack known as angler phishing. Today, it is not unusual for businesses to interact with their followers and customers on various social media platforms like Twitter and Facebook. Customers are also quick to take to social media to express their grievances about a particular service or product. Cybercriminals leverage this to trick customers using fake corporate social media accounts. Check out this example:
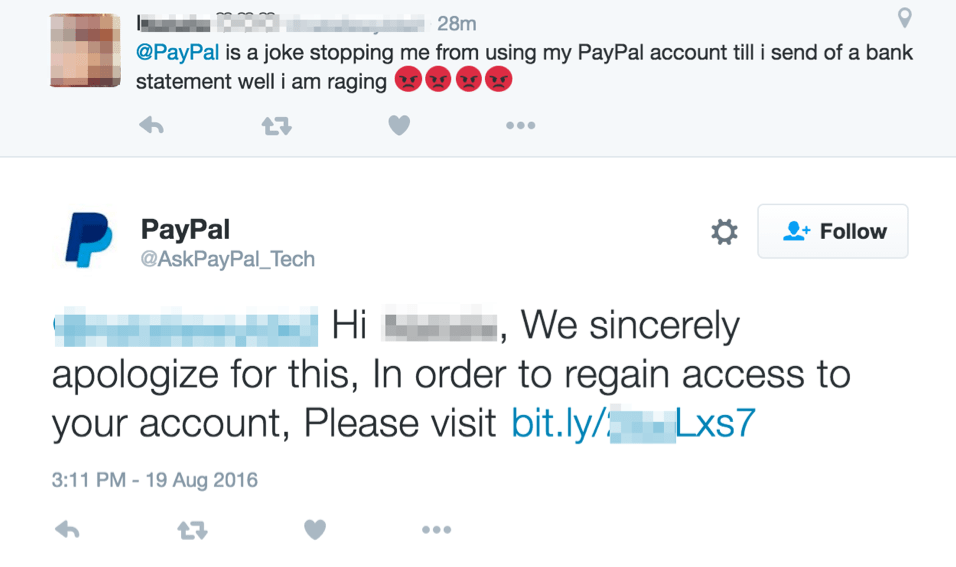
Source: proofpoint
This image depicts a Twitter angler phishing attack in which stolen branding was used to create a convincing trap that can lure users to enter their PayPal credentials into a fake website, giving scammers direct access to their accounts and funds.
Phishing Prevention
How to Tell if You're Being Phished
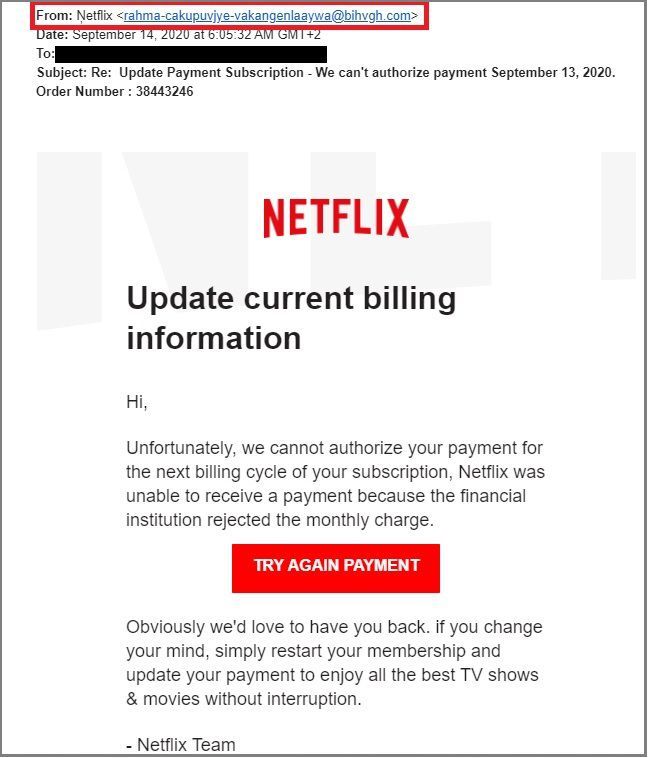
- Creating a feeling of urgency - Phishing emails often lead with phrases that urge you to take immediate action. For instance, they may tell you that your account is about to expire or that you have only a few minutes to respond in order to trick you into acting fast;
- Eye-catching subject lines with lucrative offers - Many emails claim that you have just won a very lavish prize;
- Fake links - Links can be deceptive. Most often, they are spelled slightly incorrectly to mislead the targets. Inspect links carefully and hover your mouse over the link to reveal the actual url;
- Unusual or unexpected sender - You might receive such emails completely out of the blue from someone unknown or suspicious;
- Malicious attachments - If you receive an email with an unexpected attachment or one that makes little sense, don’t download it as it may contain a virus or malware that could infect your system.
When it comes to phishing, the most serious risk is not being able to detect signs of a scam. Remember to always double-check your emails to make sure that they aren’t traps.
Phishing Prevention Tips
In addition to recognizing signs of a phishing attack, here are some more tips you can follow to prevent it:
Don’t click on random links
When you’re on a trusted website, it is okay to click the links. However, when you receive a suspicious link in a random email or text message, refrain from clicking on it. Hovering over a potential dangerous link can show you exactly where it leads.
Verify Website Security
Check for “https” and a closed lock sign at the beginning of the website name before you submit any information on it. Additionally, check for the website’s security certificate as well.
Check Your Online Accounts on a Regular Basis
Check in with each of your online accounts on a regular basis, even if it isn't really necessary. Also make it a point to change your passwords from time to time. When you don’t use an account for a long period of time, a hacker could take advantage of it.
Regularly Update Your Browser
The moment an update for your browser is available, install it. These updates are released for security vulnerabilities that hackers discover and exploit. Always look out for new update alerts.
Block Pop-Ups
Very often, pop-up windows are phishing attempts. Many browsers let you block pop-ups so that they don’t show up on your screen. However, if you do come across a pop-up, click on the “x” button on top to close it. Avoid clicking any other buttons that say “allow” or “cancel”.
Use an Anti-Phishing Solution
Anti-Phishing solutions use a variety of techniques to identify and block phishing emails. Some of them scan the content of incoming and internal emails for any language that could indicate a potential phishing or impersonation attack. Other anti-phishing technology scans email links and attachments and prevents users from accessing them if they are found to be suspicious.
Biggest Real World Phishing Attacks
Facebook and Google
Sony Pictures
The attackers phished some of the top Sony executives for months, stole their private and confidential data, and even information about films that weren’t yet released. They also went to the extent of using a wiper malware to wipe out Sony’s computer infrastructure.
This hacker group was later linked to a state-sponsored North Korean group whose primary goal was to force Sony Pictures to take down The Interview, a film about assassinating the North Korean leader, Kim Jong Un.
Crelan Bank
An attacker impersonated the CEO of the Belgian company, and asked an employee to transfer funds to an account that the attacker controlled. The incident caused €75.6 million in damages, which may include remediation costs. This attack came soon after a similar attack in 2016, on FACC, an Austrian aerospace parts manufacturer.
Conclusion
83% of organizations reported experiencing a phishing attack in 2021. An additional 6 billion attacks are expected in 2022. Hackers are constantly sharpening their abilities and launching bigger and better attacks. Each day, millions of phishing emails are sent, and every once in a while some of them are going to slip right through your security system into your company’s network.
Train your staff to be your biggest asset when it comes to phishing prevention. Because while appropriate security controls are essential, the final defense against phishing lies in the hands of your employees.
How to Use Evolve to Prevent Phishing
EvolveCTI automatically incorporates cyber threat intelligence into your security infrastructure to proactively protect your company. One of its many key features is spam and phishing intelligence to ensure that you don’t fall victim to phishing attacks. In addition, EvolveID monitors your business email accounts and domain names to identify any breached passwords.
If you wish to see how these Evolve products work to secure your company from phishing attacks,
schedule a demo
with one of our experts today.






